What is a Viva sensor?
Powered by advanced AI computer vision, each Viva sensor provides highly accurate multimodal transportation data. Outperforming traditional monitoring technology, real-time data is easy to access, secure and comprehensive, offering insights into movements, speeds, behaviors, near miss incidents, traffic flow and more.
Viva sensors can be permanently installed for long-term projects that may include before and after data for example or relocated for shorter data requirements. Each sensor requires AC power with solar options also available.
Why Choose Viva?







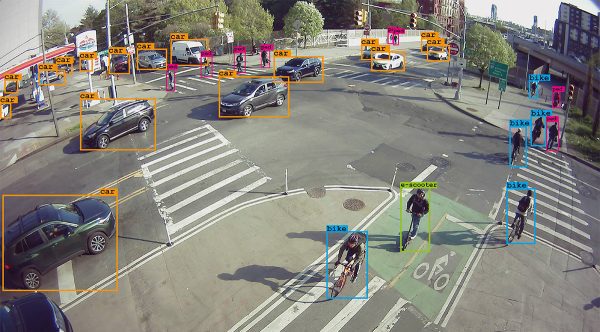
Viva sensor classifications
With additional modes of transportation constantly entering our network, we are continuously training and developing our AI to identify new classifications. Each classification released is trained on up to 10,000 images in order to gain and maintain optimum levels of accuracy. Viva users are provided with instant access to new classification releases and those in training at no extra cost via the Viva dashboard.
Classifications include: Vehicle, Pedestrian, Bicyclist, E-scooter, Motorcycle, Bus
Classifications in-training: Taxi, Cargo Bike, Wheelchair, Jogger, Pushchair plus much more
Viva sensor capabilities
Counts – Number of road users which have crossed a countline and their direction of travel.
Dwell Times – Length of time that each road user has spent stopped in a zone.
Near Miss – Identify potential conflicts between road users and the root cause of the event.
Occupancy – Number of road users detected in a zone with the ability to differentiate between moving and stopped road users.
Sensor Image – A real-time privacy-protected image capture of the sensor’s field of view.
Speed – The instantaneous speed of a road user as they cross a countline.
Tracks – Movement path taken by every road user during a specified time range.
Turning Counts – Number of road users who have moved from one zone to another zone.
Why upgrade to Viva from legacy methods?
Traditional traffic monitoring technology is unable to accurately process the variety and volume of transport using our roads today. The majority of cities were built around the car. However, the momentum in modal shift, away from private vehicles towards more active transportation, requires cities to adapt to meet the network demands of today.
Incumbent technologies, such as induction loops and radar, predominantly focus on motorized, vehicular data capture. When tasked with gathering data on other modes, accuracy is reduced. They are limited in the datasets they can capture, namely Classified Counts and Speed.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
