Viva data is supporting a landmark road safety initiative
Like many councils across the UK, Cardiff Council, supported by Welsh Government and Transport for Wales, wants to encourage more active and sustainable travel. Making roads safer for pedestrians and other vulnerable modes is essential to achieving this.
A trial of non-prescribed ‘simple’ zebra crossings on three side roads has been commissioned by Welsh Government. Viva data is supporting the trial’s evaluation.
Viva monitoring approach
Two sensors are installed at each crossing site. Wide angle-lenses are used to capture movement data occurring on the zebra crossing itself and motor vehicle and cyclist turning data from the main road onto the side road at the approach to the crossing.

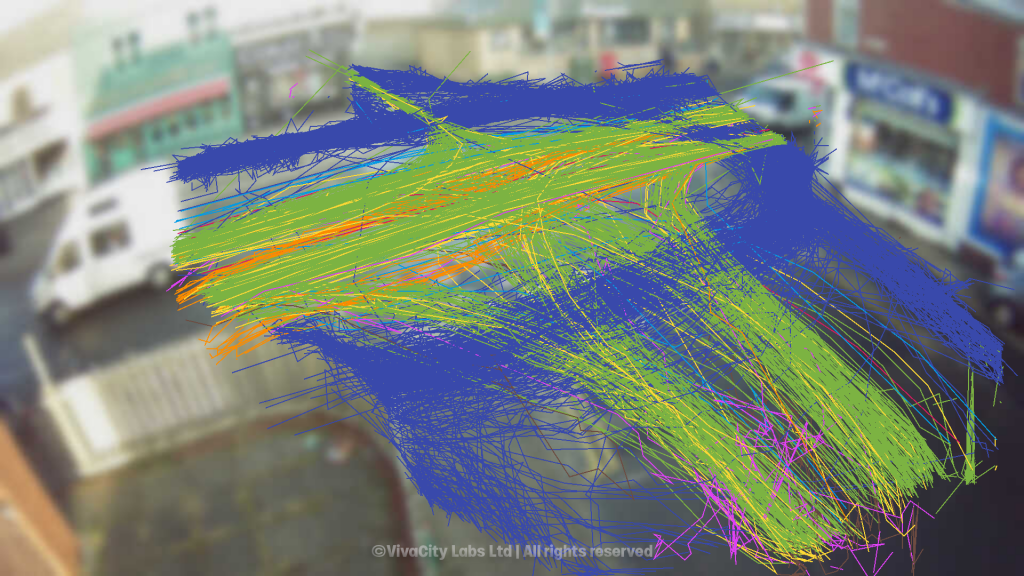
The area surrounding the crossing is divided into seven sections within the sensor’s field view.
Movement and speed data from these segments illustrate road user behaviors and patterns in response to the crossings and road safety consequences of their installation.
These datasets were provided to TRL for analysis.
Key insights the data will identify include the Give Way behaviors of vehicles and cyclists when a pedestrian is using the crossing and how the presence of the side zebras is influencing where pedestrians cross the road.
In addition to this it will also be possible to understand how vehicles alter their behavior on the approach to the crossing, and to what degree this changed following the installation of the crossing.
Prescribed vs Non-prescribed Zebra Crossings

| Feature | Prescribed | Non-prescribed |
|---|---|---|
| Black and white stripes across the carriageway | Yes | Yes |
| Give way lines on either side | Yes | Yes |
| An illuminated Belisha beacon at each end of the crossing | Yes | No |
| A line of studs marking the crossing area | Yes | No |
| Zigzag marks on the approach | Yes | No |
Benefits of non-prescribed zebra crossings
A prescribed zebra crossing with associated infrastructure can cost up to £40,000 to install. Without studs and Belisha beacons, a non-prescribed zebra crossing can be installed much faster and at a fraction of the cost.
Whatsmore, because non-prescribed zebra crossings forego zigzag marks on the approach of the zebra, they can be installed at the mouth of a junction on side roads – where pedestrians are most likely to cross the road.
Data guides future road safety regulations
Currently there is no ‘DMRB standard’ for simplified zebras in Wales. Data from this trial will be used to determine if there is a strong business case for introducing clear regulations for simplified zebra crossings to make it easier for Welsh councils to prescribe them.
Updates to the Highway Code made in January 2022 had the overarching theme of improving the safety of the most vulnerable road users, underpinned by the formalised hierarchy of road users concept. This hierarchy places road user type most at risk in the event of a collision – pedestrians – at the top.
Employing the hierarchy concept in a use case particularly relevant to the side road zebra crossing trial in Cardiff, the Code update clarified that if people have started crossing and traffic wants to turn into a road, pedestrians crossing have priority and traffic must give way.
It’s essential that accurate, comprehensive road user data that captures behaviors and interactions across every hierarchical layer, is at the heart of road safety policy and infrastructure decision-making. Intervention performance analysis from trials like this one in Cardiff, are key to road safety improvements that encourage active transportation and a sustainable road network for all.
Learn more about the Side Road Zebra trial here: Simple Zebra Crossing Trial – Cardiff Council
Like our content? Sign up to our newsletter and receive the latest updates in your inbox.
Sign-Up